Table of Contents Show
✍️ AI is summarizing:
Are you a runner looking to improve your performance and overall health? Understanding the role of macronutrients and micronutrients in the best diet for runners is crucial. In this article, we will explore the importance of macronutrients, such as protein, fat, and carbohydrates, as well as micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, in a runner’s diet.
Related post:
- Running Nutrition Tips: Fuelling Strategies for Runners
- Essential Marathon Nutrition: What to Eat the Night Before
- The Best Food for Long Runs: Optimize Your Performance
Macronutrients and micronutrients in the best diet for runners
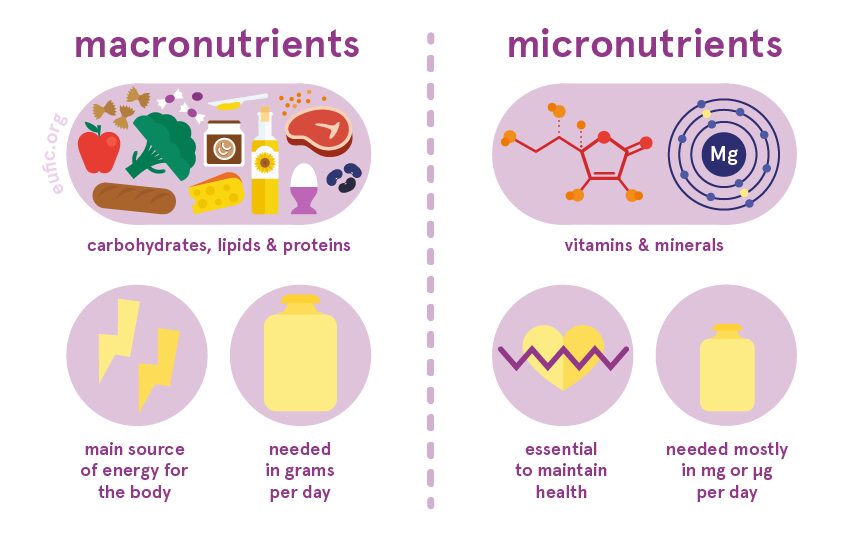
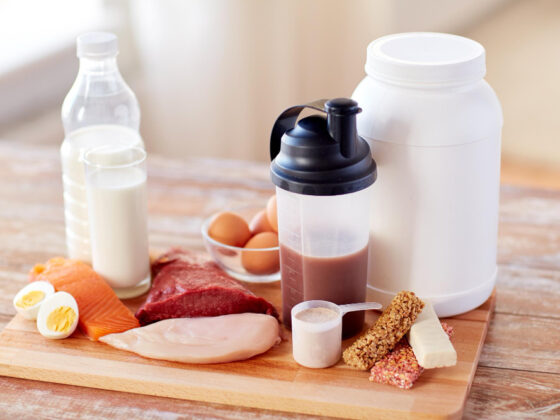
Macronutrients are the nutrients that our bodies need in large amounts, including protein, fat, and carbohydrates—key components of the best diet for runners. These nutrients provide the energy required for physical activities and optimal performance. On the other hand, micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are needed in smaller amounts, but they are still essential for various bodily functions, including muscle recovery and immune support.
How nutrients impact weight management in a runner’s diet
Research has shown that consuming nutrient-dense foods can help manage weight. When you replace high-energy density foods with those that are lower in density, such as fruits and vegetables, you can better manage your weight. Additionally, consuming a diet that is low in micronutrients can lead to normal body processes not occurring at the most efficient level, resulting in increased risks of age-related and chronic diseases.
Oxidative stress and the importance of the best diet for runners
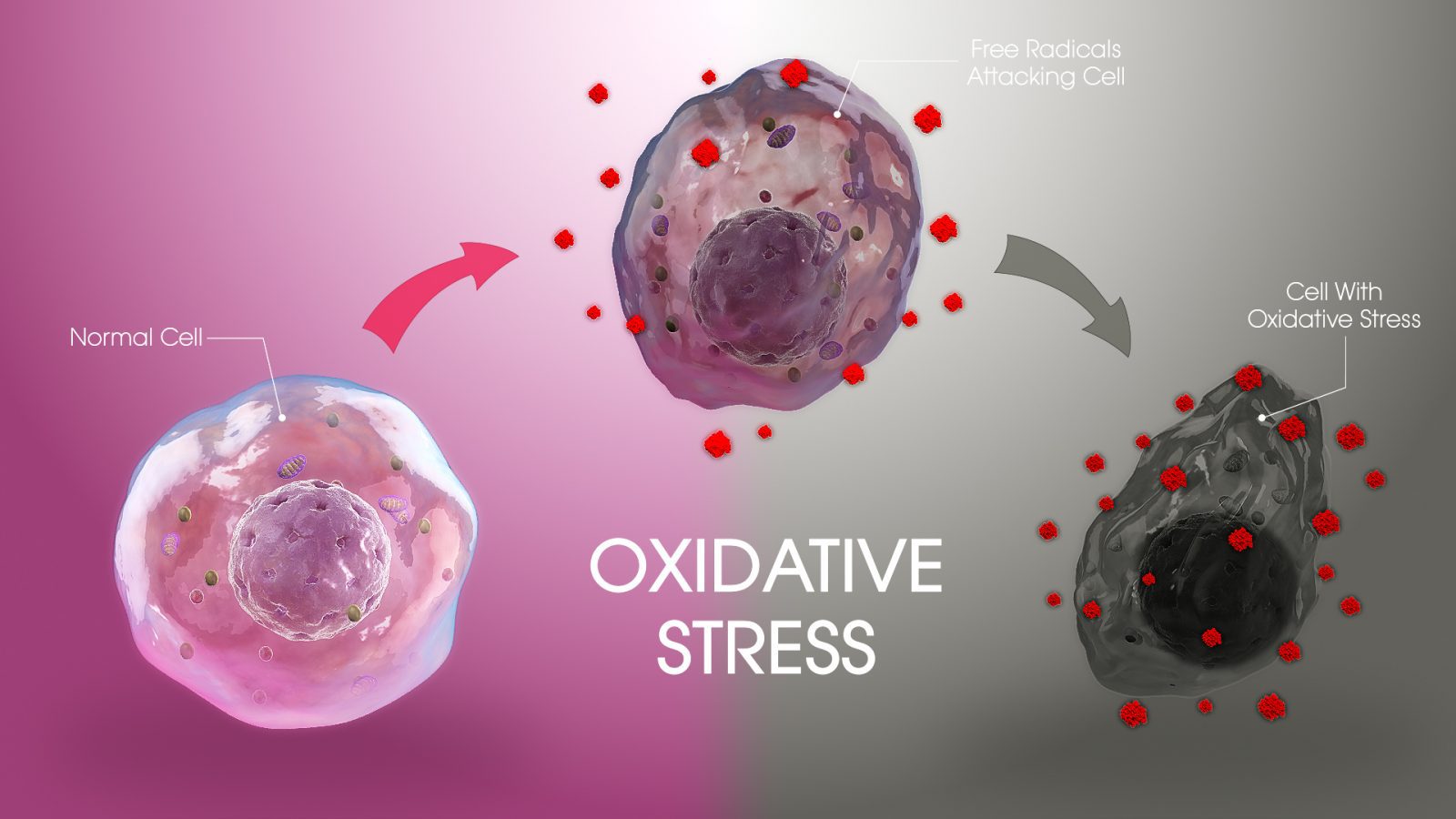
Runners are more susceptible to oxidative stress due to their increased breathing rate during training and competitions. This process can lead to the production of highly reactive molecules within cells, potentially causing damage. However, incorporating the best diet for runners, which includes vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, can help combat oxidative stress and support recovery.
Key nutritional needs in the best diet for runners
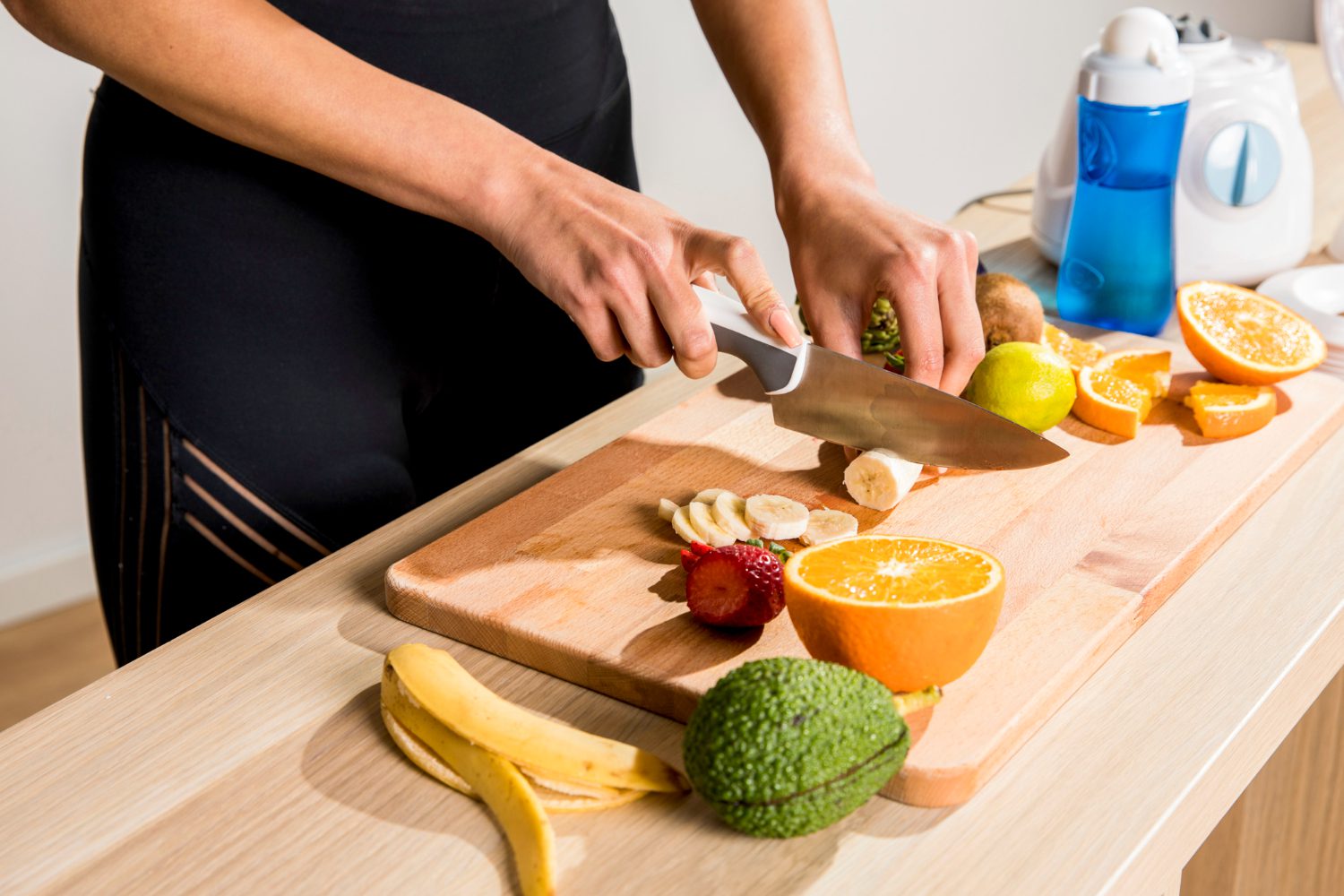

For optimal performance, runners should consume a variety of vitamins, minerals, complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats, all of which are fundamental components of the best diet for runners.
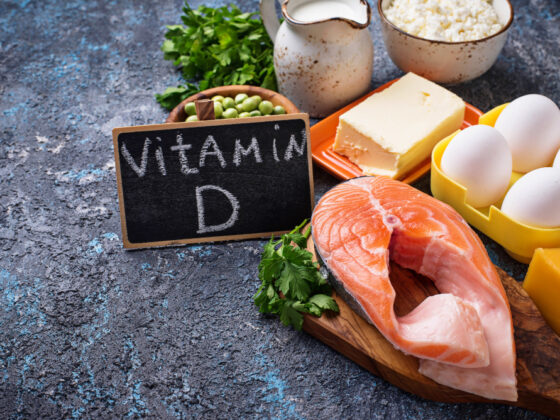
Foods such as kale, spinach, salmon, low-fat dairy products, and nuts provide essential nutrients that promote endurance, muscle repair, and energy production. Additionally, adequate Vitamin D intake obtained from sunshine or fortified foods is important for bone health and overall athletic performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the best diet for runners is essential for sustaining energy, improving endurance, and maintaining long-term health. By consuming a balanced diet rich in both macronutrients and micronutrients, runners can enhance their performance and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your running journey, prioritizing nutrient-dense foods is key to keeping your body in peak condition. Follow ExoTrails on Facebook for your daily dose of travel inspiration and tips.












